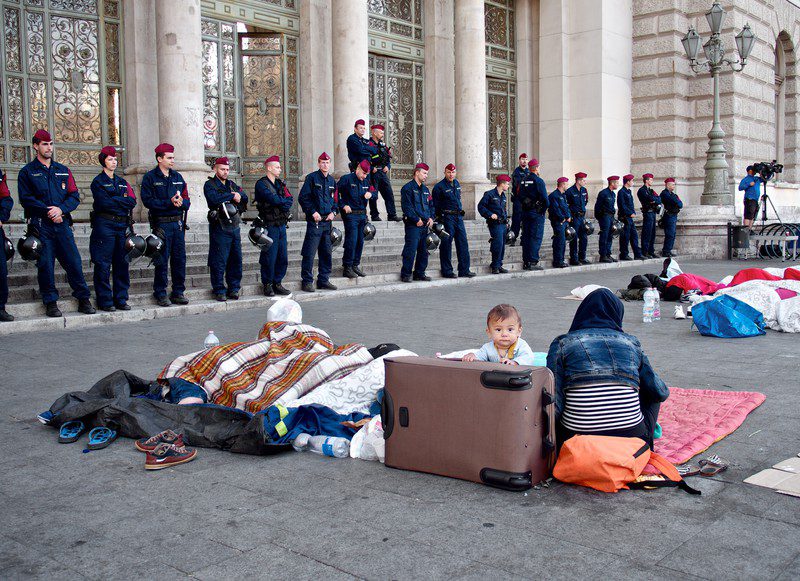
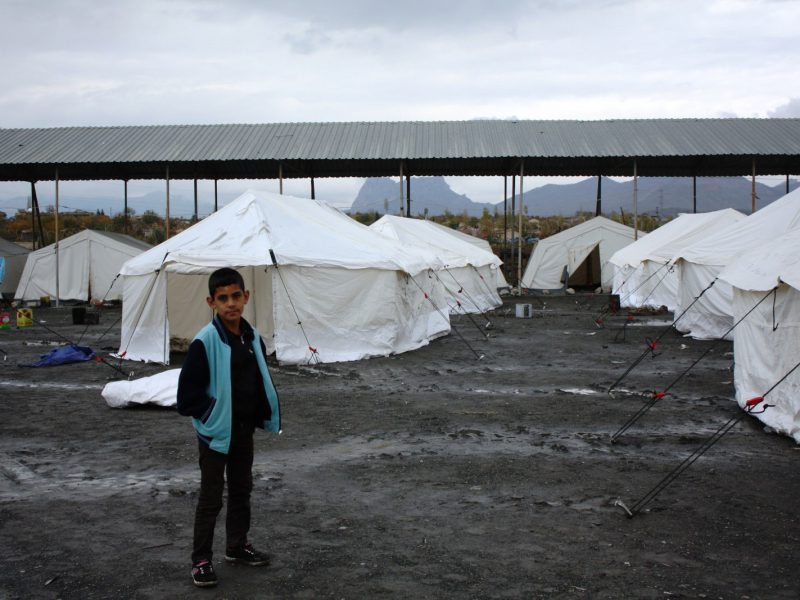
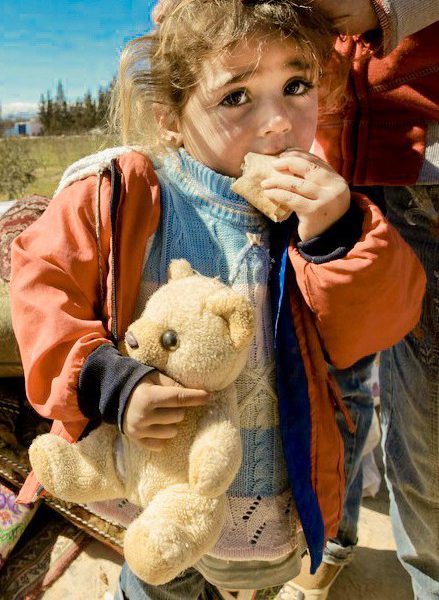
Ersatz Environmentalism VW-Style
World’s export champion Germany knew but did nothing to question the integrity of one of their biggest producers. The revelations cast a dark shadow on the entire auto industry. What is worse, Germany-led Europe in its entirety now appears shrouded in a foul smell. The Union that seemed the bastion of environmentalism and of regulations protecting the rights and health of consumers is now being openly ridiculed by US neoliberals in the media.