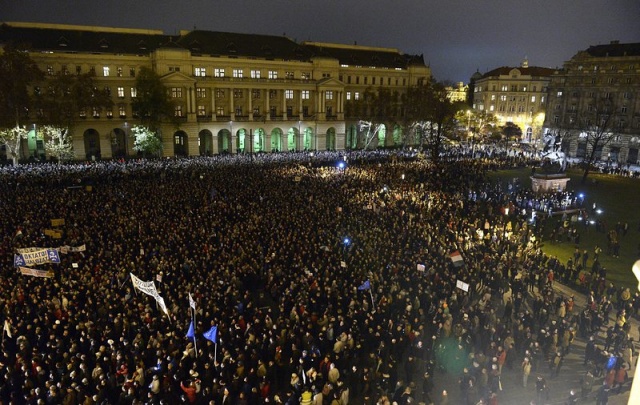
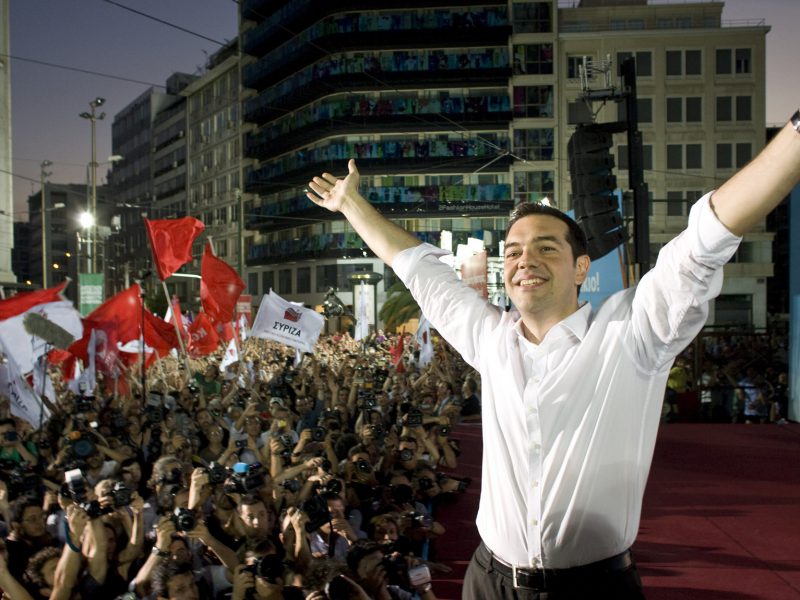
Chaos has always been a scenario for Greece, ever since the bailout. The mix was there: a bankrupt country, crippling unemployment, violent riots, weekly strikes, neo-Nazis in parliament, a rapid decline in living standards that turned into a humanitarian emergency. Outside Greece, in public analysis and private conversations, the possibility of the destabilisation of democracy came up every now and then, some kind of coup that would send the country to the extreme left or right. For those who indulged in these cassandric predictions the rise of leftist Syriza was a vindication: surely this is a rogue party, self-positioned on the Radical Left, with communist roots, and a populist rhetoric? Discussion of the Greek problem has always involved a degree of fear-mongering, which is useful in the manipulation of public opinion, but rather redundant in adding any nuance to our understanding of a foreign context. A useful key-phrase, if one truly wishes to understand Greece in crisis, is “structural reforms”.