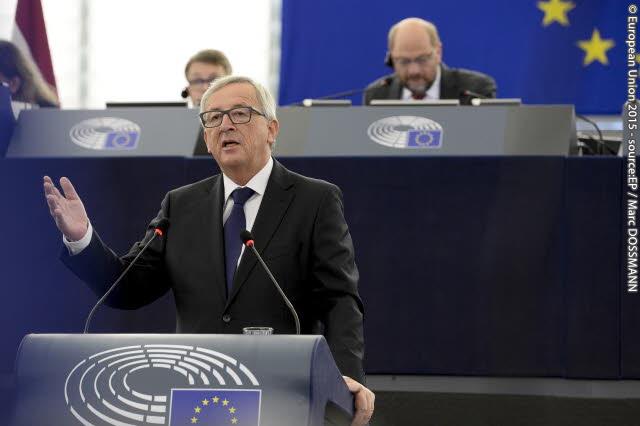
First State of the Union address to the European Parliament by European Commission President Jean-Claude Juncker
State of the Union 2015: Time for Honesty, Unity and Solidarity
Strasbourg, 9 September 2015
Mr President,
Honourable Members of the European Parliament,
Today is the first time during my mandate as President of the European Commission that I have the honour to address this House on the State of our European Union.
I would therefore like to recall the political importance of this very special institutional moment.
The State of the Union address is foreseen explicitly by the Framework Agreement that governs the relations between the European Parliament and the European Commission. This Agreement provides that “[e]ach year in the first part-session of September, a State of the Union debate will be held in which the President of the Commission shall deliver an address, taking stock of the current year and looking ahead to priorities for the following years. To that end, the President of the Commission will in parallel set out in writing to Parliament the main elements guiding the preparation of the Commission Work Programme for the following year.”
The State of the Union address requires the President of the Commission to take stock of the current situation of our European Union and to set priorities for the work ahead.
And it launches the interinstitutional process leading to a new Work Programme of the European Commission for the year ahead.
Together with Frans Timmermans, my First Vice-President, this morning I sent a letter to the Presidents of both branches of the European legislator: to President Martin Schulz, and to Luxembourg’s Prime Minister Xavier Bettel, who currently holds the rotating Presidency of the Council. This letter sets out in detail the numerous actions the Commission intends to take by means of legislation and other initiatives, from now until the end of 2016. We are proposing an ambitious, focused, and intense legislative agenda that will require Commission, Parliament and Council to work closely and effectively together.
I will not go into the details of our legislative agenda now. We will have a structured dialogue with the Parliament and the Council on this in the weeks to come.
But I feel that today is not the moment to speak about all this.
I am the first President of the Commission whose nomination and election is the direct result of the outcome of the European Parliament elections in May 2014.
Having campaigned as a lead candidate, as Spitzenkandidat, in the run up to the elections, I had the opportunity to be a more political President.
This political role is foreseen by the Treaties, by means of which the Member States made the Commission the promoter of the general interest of the Union. But the crisis years have diminished this understanding.
This is why I said last September before this House that I wanted to lead a political Commission. A very political Commission.
I said this not because I believe we can and should politicise everything.
I said it because I believe the immense challenges Europe is currently facing – both internally and externally – leave us no choice but to address them from a very political perspective, in a very political manner and having the political consequences of our decisions very much in mind.
Recent events have confirmed the urgent need for such a political approach in the European Union.
This is not the time for business as usual.
This is not the time for ticking off lists or checking whether this or that sectorial initiative has found its way into the State of the Union speech.
This is not the time to count how many times the word social, economic or sustainable appears in the State of the Union speech.
Instead, it is time for honesty.
It is time to speak frankly about the big issues facing the European Union.
Because our European Union is not in a good state.
There is not enough Europe in this Union.
And there is not enough Union in this Union.
We have to change this. And we have to change this now.
The Refugee Crisis: The Imperative to Act as a Union
Whatever work programmes or legislative agendas say: The first priority today is and must be addressing the refugee crisis.
Since the beginning of the year, nearly 500,000 people have made their way to Europe. The vast majority of them are fleeing from war in Syria, the terror of the Islamic State in Libya or dictatorship in Eritrea. The most affected Member States are Greece, with over 213,000 refugees, Hungary, with over 145,000, and Italy, with over 115,000.
The numbers are impressive. For some they are frightening.
But now is not the time to take fright. It is time for bold, determined and concerted action by the European Union, by its institutions and by all its Member States.
This is first of all a matter of humanity and of human dignity. And for Europe it is also a matter of historical fairness.
We Europeans should remember well that Europe is a continent where nearly everyone has at one time been a refugee. Our common history is marked by millions of Europeans fleeing from religious or political persecution, from war, dictatorship, or oppression.
Huguenots fleeing from France in the 17th century.
Jews, Sinti, Roma and many others fleeing from Germany during the Nazi horror of the 1930s and 1940s.
Spanish republicans fleeing to refugee camps in southern France at the end of the 1930s after their defeat in the Civil War.
Hungarian revolutionaries fleeing to Austria after their uprising against communist rule was oppressed by Soviet tanks in 1956.
Czech and Slovak citizens seeking exile in other European countries after the oppression of the Prague Spring in 1968.
Hundreds and thousands were forced to flee from their homes after the Yugoslav wars.
Have we forgotten that there is a reason there are more McDonalds living in the U.S. than there are in Scotland? That there is a reason the number of O’Neills and Murphys in the U.S. exceeds by far those living in Ireland?
Have we forgotten that 20 million people of Polish ancestry live outside Poland, as a result of political and economic emigration after the many border shifts, forced expulsions and resettlements during Poland’s often painful history?
Have we really forgotten that after the devastation of the Second World War, 60 million people were refugees in Europe? That as a result of this terrible European experience, a global protection regime – the 1951 Geneva Convention on the status of refugees – was established to grant refuge to those who jumped the walls in Europe to escape from war and totalitarian oppression?
We Europeans should know and should never forget why giving refuge and complying with the fundamental right to asylum is so important.
I have said in the past that we are too seldom proud of our European heritage and our European project.
Yet, in spite of our fragility, our self-perceived weaknesses, today it is Europe that is sought as a place of refuge and exile.
It is Europe today that represents a beacon of hope, a haven of stability in the eyes of women and men in the Middle East and in Africa.
That is something to be proud of and not something to fear.
Europe today, in spite of many differences amongst its Member States, is by far the wealthiest and most stable continent in the world.
We have the means to help those fleeing from war, terror and oppression.
I know that many now will want to say that this is all very well, but Europe cannot take everybody.
It is true that Europe cannot house all the misery of the world. But let us be honest and put things into perspective.
There is certainly an important and unprecedented number of refugees coming to Europe at the moment. However, they still represent just 0.11% of the total EU population. In Lebanon, refugees represent 25% of the population. And this in a country where people have only one fifth of the wealth we enjoy in the European Union.
Let us also be clear and honest with our often worried citizens: as long as there is war in Syria and terror in Libya, the refugee crisis will not simply go away.
We can build walls, we can build fences. But imagine for a second it were you, your child in your arms, the world you knew torn apart around you. There is no price you would not pay, there is no wall you would not climb, no sea you would not sail, no border you would not cross if it is war or the barbarism of the so-called Islamic State that you are fleeing.
So it is high time to act to manage the refugee crisis. There is no alternative to this.
There has been a lot finger pointing in the past weeks. Member States have accused each other of not doing enough or of doing the wrong thing. And more often than not fingers have been pointed from national capitals towards Brussels.
We could all be angry about this blame-game. But I wonder who that would serve. Being angry does not help anyone. And the attempt of blaming others is often just a sign that politicians are overwhelmed by unexpected events.
Instead, we should rather recall what has been agreed that can help in the current situation. It is time to look at what is on the table and move swiftly forwards.
We are not starting anew. Since the early 2000s, the Commission has persistently tabled legislation after legislation, to build a Common European Asylum System. And the Parliament and the Council have enacted this legislation, piece by piece. The last piece of legislation entered into force just in July 2015.
Across Europe we now have common standards for the way we receive asylum seekers, in respect of their dignity, for the way we process their asylum applications, and we have common criteria which our independent justice systems use to determine whether someone is entitled to international protection.
But these standards need to be implemented and respected in practice. And this is clearly not yet the case, we can see this every day on television. Before the summer, the Commission had to start a first series of 32 infringement proceedings to remind Member States of what they had previously agreed to do. And a second series will follow in the days to come. European laws must be applied by all Member States – this must be self-evident in a Union based on the rule of law.
Common asylum standards are important, but not enough to cope with the current refugee crisis. The Commission, the Parliament and the Council said this in spring. The Commission tabled a comprehensive European Agenda on Migration in May. And it would be dishonest to say that nothing has happened since then.
We tripled our presence at sea. Over 122,000 lives have been saved since then. Every life lost is one too many, but many more have been rescued that would have been lost otherwise – an increase of 250%. 29 Member States and Schengen Associated countries are participating in the joint operations coordinated by Frontex in Italy, Greece and Hungary. 102 guest officers from 20 countries; 31 ships; 3 helicopters; 4 fixed wing aircrafts; 8 patrol cars, 6 thermos-vision vehicles and 4 transport vehicles – that is a first measure of European solidarity in action, even though more will have to be done.
We have redoubled our efforts to tackle smugglers and dismantle human trafficker groups. Cheap ships are now harder to come by, leading to less people putting their lives in peril in rickety, unseaworthy boats. As a result, the Central Mediterranean route has stabilised at around 115,000 arriving during the month of August, the same as last year. We now need to achieve a similar stabilisation of the Balkans route, which has clearly been neglected by all policy-makers.
The European Union is also the number one donor in the global efforts to alleviate the Syrian refugee crisis. Around €4 billion have been mobilised by the European Commission and Member States in humanitarian, development, economic and stabilisation assistance to Syrians in their country and to refugees and their host communities in neighbouring Lebanon, Jordan, Iraq, Turkey and Egypt. Indeed just today we launched two new projects to provide schooling and food security to 240,000 Syrian refugees in Turkey.
We have collectively committed to resettling over 22,000 people from outside of Europe over the next year, showing solidarity with our neighbours. Of course, this remains very modest in comparison to the Herculean efforts undertaken by Turkey, Jordan and Lebanon, who are hosting over 4 million Syrian refugees. I am encouraged that some Member States are showing their willingness to significantly step up our European resettlement efforts. This will allow us very soon to come forward with a structured system to pool European resettlement efforts more systematically.
Where Europe has clearly under-delivered, is on common solidarity with regard to the refugees who have arrived on our territory.
To me, it is clear that the Member States where most refugees first arrive – at the moment, these are Italy, Greece and Hungary – cannot be left alone to cope with this challenge.
This is why the Commission already proposed an emergency mechanism in May, to relocate initially 40,000 people seeking international protection from Italy and Greece.
And this is why today we are proposing a second emergency mechanism to relocate a further 120,000 from Italy, Greece and Hungary.
This requires a strong effort in European solidarity. Before the summer, we did not receive the backing from Member States I had hoped for. But I see that the mood is turning. And I believe it is high time for this.
I call on Member States to adopt the Commission proposals on the emergency relocation of altogether 160,000 refugees at the Extraordinary Council of Interior Ministers on 14 September. We now need immediate action. We cannot leave Italy, Greece and Hungary to fare alone. Just as we would not leave any other EU Member State alone. For if it is Syria and Libya people are fleeing from today, it could just as easily be Ukraine tomorrow.
Europe has made make the mistake in the past of distinguishing between Jews, Christians, Muslims. There is no religion, no belief, no philosophy when it comes to refugees.
Do not underestimate the urgency. Do not underestimate our imperative to act. Winter is approaching – think of the families sleeping in parks and railway stations in Budapest, in tents in Traiskirchen, or on shores in Kos. What we will become of them on cold, winter nights?
Of course, relocation alone will not solve the issue. It is true that we also need to separate better those who are in clear need of international protection and are therefore very likely to apply for asylum successfully; and those who are leaving their country for other reasons which do not fall under the right of asylum. This is why today the Commission is proposing a common EU list of safe countries of origin. This list will enable Member States to fast track asylum procedures for nationals of countries that are presumed safe to live in. This presumption of safety must in our view certainly apply to all countries which the European Council unanimously decided meet the basic Copenhagen criteria for EU membership – notably as regards democracy, the rule of law, and fundamental rights. It should also apply to the other potential candidate countries on the Western Balkans, in view of their progress made towards candidate status.
I am of course aware that the list of safe countries is only a procedural simplification. It cannot take away the fundamental right of asylum for asylum seekers from Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia, Kosovo, Montenegro, Serbia, and Turkey. But it allows national authorities to focus on those refugees which are much more likely to be granted asylum, notably those from Syria. And this focus is very much needed in the current situation.
I also believe that beyond the immediate action needed to address current emergencies, it is time we prepare a more fundamental change in the way we deal with asylum applications – and notably the Dublin system that requires that asylum applications be dealt with by the first country of entry.
We need more Europe in our asylum policy. We need more Union in our refugee policy.
A true European refugee and asylum policy requires solidarity to be permanently anchored in our policy approach and our rules. This is why, today, the Commission is also proposing a permanent relocation mechanism, which will allow us to deal with crisis situations more swiftly in the future.
A common refugee and asylum policy requires further approximation of asylum policies after refugee status is granted. Member States need to take a second look at their support, integration and inclusion policies. The Commission is ready to look into how EU Funds can support these efforts. And I am strongly in favour of allowing asylum seekers to work and earn their own money whilst their applications are being processed.
A united refugee and asylum policy also requires stronger joint efforts to secure our external borders. Fortunately, we have given up border controls between the Member States of the Schengen area, to guarantee free movement of people, a unique symbol of European integration. But the other side of the coin to free movement is that we must work together more closely to manage our external borders. This is what our citizens expect. The Commission said it back in May, and I said it during my election campaign: We need to strengthen Frontex significantly and develop it into a fully operational European border and coast guard system. It is certainly feasible. But it will cost money. The Commission believes this is money well invested. This is why we will propose ambitious steps towards a European Border and Coast Guard before the end of the year.
A truly united, European migration policy also means that we need to look into opening legal channels for migration. Let us be clear: this will not help in addressing the current refugee crisis. But if there are more, safe and controlled roads opened to Europe, we can manage migration better and make the illegal work of human traffickers less attractive. Let us not forget, we are an ageing continent in demographic decline. We will be needing talent. Over time, migration must change from a problem to be tackled to a well-managed resource. To this end, the Commission will come forward with a well-designed legal migration package in early 2016.
A lasting solution will only come if we address the root causes, the reasons why we are currently facing this important refugee crisis. Our European foreign policy must be more assertive. We can no longer afford to be ignorant or disunited with regard to war or instability right in our neighbourhood.
In Libya, the EU and our Member States need to do more to engage with regional partners to make sure a Government of National Accord is in place soon. We should be prepared to help, with all EU instruments available, such a government to deliver security and services to the population as soon as it is in place. Our EU development and humanitarian support will have to be immediate and comprehensive.
I would also like to point out that we are entering the fifth year of the Syrian crisis with no end in sight. So far, the international community has failed the Syrian people. Europe has failed the Syrian people.
Today I call for a European diplomatic offensive to address the crises in Syria and in Libya. We need a stronger Europe when it comes to foreign policy. And I am very glad that Federica Mogherini, our determined High Representative, has prepared the ground for such an initiative with her diplomatic success in the Iran nuclear talks. And that she stands ready to work closely together with our Member States towards peace and stability in Syria and Libya.
To facilitate Federica’s work, today the Commission is proposing to establish an emergency Trust Fund, starting with €1.8 billion from our common EU financial means to address the crises in the Sahel and Lake Chad regions, the Horn of Africa, and the North of Africa. We want to help create lasting stability, for instance by creating employment opportunities in local communities, and thereby address the root causes of destabilisation, forced displacement and illegal migration. I expect all EU Member States to pitch in and match our ambitions.
I do not want to create any illusions that the refugee crisis will be over any time soon. It will not. But pushing back boats from piers, setting fire to refugee camps, or turning a blind eye to poor and helpless people: that is not Europe.
Europe is the baker in Kos who gives away his bread to hungry and weary souls. Europe is the students in Munich and in Passau who bring clothes for the new arrivals at the train station. Europe is the policeman in Austria who welcomes exhausted refugees upon crossing the border. This is the Europe I want to live in.
The crisis is stark and the journey is still long. I am counting on you, in this House, and on all Member States to show European courage going forward, in line with our common values and our history.
A new start for Greece, for the euro area and for the European economy
Mr President, Honourable Members,
I said I want to talk about the big issues today. This is why this State of the Union speech needs to address the situation in Greece, as well as the broader lessons from the fifth year of Greek crisis the impact of which continues to be felt in the Eurozone and in the European economy and society as a whole.
Since the start of the year, the talks on Greece have tested all our patience. A lot of time and a lot of trust was lost. Bridges were burnt. Words were said that cannot easily be taken back.
We saw political posturing, bickering and insults carelessly bandied about.
Too often, we saw people thinking they can impose their views without a wayward thought for another’s point of view.
We saw democracies in the Eurozone being played against each other. The recovery and creation of jobs witnessed last year in Greece vanished during these months.
Collectively, we looked into the abyss.
And it was once more only when we were at the brink that we were able to see the bigger picture and to live up to our responsibilities.
In the end, a deal was reached, commitments were adhered to and implemented. Trust has started to be regained, even though it remains very fragile.
I am not proud of every aspect of the results achieved. However, I am proud of the teams in the European Commission who worked day and night until late in August, relentlessly, to bridge the gap between far-flung positions and to bring about solutions in the interest of Europe and of the Greek people.
I know that not everybody was happy with what the Commission did.
Many Greek politicians were not happy that we insisted on reforms in Greece, notably as regards the unsustainable pension system and the unfair tax regime.
Many other European politicians could not understand why the Commission continued to negotiate. Some could not understand why we did not simply leave all the talks to the technicians of the International Monetary Fund. Why we sometimes also spoke about the social side of programme commitments and amended those to take account of the effects on the most vulnerable in society. Or that I personally dared to say again and again that the euro, and membership in the euro, is meant to be irreversible.
Mr President, Honourable Members,
The Commission’s mandate in negotiations with a programme country such as Greece has a very clear basis: it is the Treaty on European Union which calls on the Commission to promote the common interest of the Union and to uphold the law. The same law includes the Treaty clause, agreed by all Member States, that qualifies membership in the euro as irrevocable.
As long as Member States have not amended the Treaties, I believe the Commission and all other EU institutions have a clear mandate and duty to do everything possible to preserve the integrity of the euro area.
The Commission has also been explicitly entrusted by the European Stability Mechanism (ESM) Treaty, ratified by all euro area Member States, with conducting programme negotiations with a Member State. We have to do this in liaison with the European Central Bank and, where possible, together with the International Monetary Fund. But we have a clear mandate to do so.
Where the Treaties talk about the Commission, I read this as meaning the Commission as an institution that is politically led by the President and the College of Commissioners. This is why I did not leave the talks with Greece to the Commission bureaucracy alone, in spite of their great expertise and the hard work they are doing. But I spoke personally to our experts regularly, often several times per day, to orient them or to adjust their work. I also ensured that every week, the situation of the negotiations in Greece was discussed at length and very politically in the meetings of the College.
Because it is not a technical question whether you increase VAT not only on restaurants, but also on processed food. It is a political and social question.
It is not a technical question, but a deeply political question, whether you increase VAT on medicines in a country where 30% of the population is no longer covered by the public health system as a result of the crisis. Or whether you cut military expenditure instead – in a country that continues to have one of the highest military expenditures in the EU.
It is certainly not a technical question whether you reduce the pensions of the poorest in society or the minimum wage; or if you instead levy a tax on Greek ship owners.
Of course, the figures in what is now the third Greek programme had to add up in the end. But we managed to do this with social fairness in mind. I read the Troika report of the European Parliament very thoroughly. I hope you can see that we have drawn the lessons from this, that we have made, for the first time, a social impact assessment of the programme. Even though I admit frankly that the Commission also had to compromise sometimes in these negotiations.
What matters to me, is that, in the end, a compromise was found which could be agreed by all 19 euro area Member States, including Greece.
After weeks of talks, small progress, repeated setbacks, many crisis moments, and often a good dose of drama, we managed to sign a new Stability Support Programme for Greece on 19 August.
Now that the new programme is in place, I want it to be a new start, for Greece and for the euro area as a whole.
Let us be very honest: We are only at the beginning of a new, long journey.
For Greece, the key now is to implement the deal which was agreed. There has to be broad political ownership for this.
I had the leaders of all the mainstream Greek political groups in my office before the final agreement was concluded. They all promised to support this agreement, and they gave first proof of their commitment when they voted for the new programme and for the first three waves of reforms in the Hellenic Parliament. I expect them to stand by their word and deliver on the agreement – whoever governs. Broad support and timely delivery of the reforms is what Greece needs, so that confidence can return both among the Greek people and to the Greek economy.
The programme is one thing, but it is not enough to put Greece on a path of sustainable growth. The Commission will stand by Greece to make sure the reforms take shape. And we will assist Greece in developing a growth strategy which is Greek owned and Greek led.
From the modernisation of the public administration and the independence of the tax authority, the Commission will provide tailor-made technical assistance, together with the help of European and international partners. This will be the main task of the new Structural Reform Support Service I established in July.
On 15 July, the Commission also put forward a proposal to limit national co-financing in Greece and to frontload funding for investment projects short of liquidity: a €35 billion package for growth. This is urgent for recovery after months of financial squeeze. This is money that will reach the Greek real economy, for businesses and authorities to invest and recruit.
The Commission worked day-in, day-out to put this on the table. National Parliaments met several times throughout the month of August. I therefore hope that the European Parliament will also play its part, in line with previous commitments. Our programme for growth in Greece has been on the table of this House for two months. If adopted, it will still take several weeks until the first euro will reach the real economy of Greece.
I call on you to follow the example of the Council, which will agree on this growth programme by the end of this month. The European Parliament should be at least as fast as the Council on this.
I said I wanted the new programme to be a new start not just for Greece but for the euro area as a whole, because there are important lessons we need to draw from the crisis that has haunted us for far too long.
The economic and social situation speaks for itself: over 23 million people are still unemployed today in the European Union, with more than half without a job for a year or more. In the euro area alone, more than 17.5 million people are without a job. Our recovery is hampered by global uncertainties. Government debt in the EU has reached more than 88% of GDP on average, and stands at almost 93% in the euro area.
The crisis is not over. It has just been put on pause.
This is not to say that nothing is happening. Unemployment figures are improving, GDP is rising at its highest rate for years, and the financing conditions of households and companies have recovered significantly. And several Member States once severely affected – like Latvia, Ireland, Spain and Portugal – which received European financial assistance are now steadily growing and consolidating their economies.
This is progress but recovery is too slow, too fragile and too dependent on our external partners.
More fundamentally, the crisis has left us with very wide differences across the euro area and the EU as a whole. It has damaged our growth potential. It has added to the long-term trend of rising inequalities. All this has fuelled doubts about social progress, the value of change and the merits of belonging together.
What we need is to recreate a process of convergence, both between Member States and within societies, with productivity, job creation and social fairness at its core.
We need more Union in our Europe.
For the European Union, and for my Commission in particular, this means two things: first, investing in Europe’s sources of jobs and growth, notably in our Single Market; and secondly, completing our Economic and Monetary Union to creating the conditions for a lasting recovery. We are acting on both fronts.
Together with you and the Member States, we brought to life the €315 billion Investment Plan for Europe, with a new European Fund for Strategic Investments (EFSI).
Less than a year after I announced this plan, we are now at a point where some of the first projects are just taking off:
40,000 households all over France will get a lower energy bill and 6,000 jobs will be created, thanks to Investment Fund-financed improved energy efficiency in buildings.
In health clinics in Barcelona, better treatment will be available to patients through new plasma derived therapies, funded by the Investment Fund.
In Limerick and other locations in Ireland, families will have improved access to primary healthcare and social services through fourteen new primary care centres. This is just the beginning, with many more projects like these to follow.
At the same time as we deploy our Investment Plan, we are upgrading our Single Market to create more opportunities for people and business in all 28 Member States. Thanks to Commission projects such as the Digital Single Market, Capital Markets Union and the Energy Union, we are reducing obstacles to activities cross-border and using the scale of our continent to stimulate innovation, connecting talents and offering a wider choice of products and services.
But we will fail in our efforts to prosper if we do not learn a hard lesson: we have not yet convinced the people of Europe and the world that our Union is not just here to survive, but can also thrive and prosper.
Let us not fool ourselves: our collective inability to provide a swift and clear answer to the Greek crisis over the last months weakened us all. It damaged the trust in our single currency and the EU’s reputation in the world.
No wind favours he who has no destined port – we need to know where we are headed.
This is the essence of the report I presented in June with the other Presidents of the European institutions on the completion of our Economic and Monetary Union.
It was self-evident for me to include President Schulz in this important work. After all, the Parliament is the heart of democracy at EU level, just as national Parliaments are the heart of democracy at national level. The European Parliament is and must remain the Parliament of the euro area. And the European Parliament, in its role as co-legislator, will be in charge of deciding on the new initiatives the Commission will propose in the months to come to deepen our Economic and Monetary Union. I am therefore glad that for the first time, we have written not a ‘Four Presidents’ Report’, but a ‘Five Presidents’ Report’.
Despite months of late-night discussions to find an agreement for Greece, we wrote this report in May and June to set out the course for a stronger future. The Five Presidents of the leading EU institutions have agreed a roadmap that should allow us to stabilise and consolidate the euro area by early 2017; and then, on the basis of a renewed convergence of our economies, to achieve more fundamental reform and move where we can from crisis resilience to new growth perspectives.
As we had expected, the Five Presidents’ Report has triggered a lively debate across Europe. Some say we need a government of the euro. Others say we need more discipline and respect of the rules. I agree with both: we need collective responsibility, a greater sense of the common good and full respect and implementation of what is collectively agreed. But I do not agree this should mean the multiplication of institutions or putting the euro on auto pilot, as if new institutions or magic rules could deliver more or better.
You cannot run a single currency on the basis of rules and statistics alone. It needs constant political assessment, as the basis of new economic, fiscal and social policy choices.
The Five Presidents’ Report includes a full agenda of work for the years to come, and I want us to move swiftly on all fronts – economic, financial, fiscal and political Union. Some efforts will have to be focused on the euro area, while others should be open to all 28 Member States, in view of their close interaction with our Single Market.
Allow me to highlight five domains where the Commission will present ambitious proposals swiftly and where we will be expecting progress already this autumn.
First: the Five Presidents agreed that we need a common system to ensure that citizens’ bank savings are always protected up to a limit of €100,000 per person and account. This is the missing part of our Banking Union.
Today, such protection schemes exist, but they are all national. What we need is a more European system, disconnected from government purses so that citizens can be absolutely sure that their savings are safe.
We all saw what happened in Greece during the summer: Citizens were – understandably – taking out their savings since they had little trust and confidence in the financial capability of the State to support its banking system. This must change.
A more common deposit guarantee system is urgently needed, and the Commission will present a legislative proposal on the first steps towards this before the end of the year.
I am of course fully aware there is no consensus on this yet. But I also know that many of you are as convinced as I am of the need to move ahead. I say to those who are more sceptical: the Commission is fully aware that there are differences in the starting positions of Member States. Some have developed and well-financed their national systems of deposit insurance. Others are still building up such systems. We need to take these differences into account. This is why the Five Presidents’ Report advocates not full mutualisation, but a new approach by means of a reinsurance system. We will present further details on this in the weeks to come.
Second: we need a stronger representation of the euro on the global scene. How is it possible that the euro area, which has the second largest currency in the world, can still not speak with one voice on economic matters in international financial institutions?
Imagine yourselves in the daily work of the International Monetary Fund for a moment. We know well how important the IMF is. Still, instead of speaking with one voice as the euro area, Belgium and Luxembourg have to agree their voting position with Armenia and Israel; and Spain sits in a joint constituency with Latin American countries.
How can it be that we – Europeans – are jointly major shareholders of global institutions such as the IMF and the World Bank and still end up acting as a minority?
How can it be that a strategically important new Infrastructure Investment Bank is created in Asia, and European governments, instead of coordinating their efforts, engage in a race who is first to become a member?
We need to grow up and put our common interests ahead of our national ones. For me, the President of the Eurogroup should be the natural spokesperson for the euro area in international financial institutions such as the IMF.
Third: we need a more effective and more democratic system of economic and fiscal surveillance. I want this Parliament, national Parliaments, as well as social partners at all levels, to be key actors in the process. I also want the interest of the euro area as a whole to be better reflected upfront in EU and national policies: the interest of the whole is not just the sum of its parts. This will be reflected in our proposals to streamline and strengthen the European Semester of economic policy coordination further.
In the future, I no longer want our recommendations for the economic orientation of the euro area as a whole to be empty words. I want them to provide real orientation, notably on the fiscal stance of the euro area.
Fourth: we need to enhance fairness in our taxation policies. This requires greater transparency and equity, for citizens and companies. We presented an Action Plan in June, the gist of which is the following: the country where a company generates its profits must also be the country of taxation.
One step towards this goal is our work on a Common Consolidated Corporate Tax Base. This simplification will make tax avoidance more difficult.
We are also working hard with the Council to conclude an agreement on the automatic exchange of information on tax rulings by the end of the year.
At the same time, we expect our investigations into the different national schemes to yield results very soon.
And we are fighting hard to get Member States to adopt the modalities of a Financial Transaction Tax by the end of the year.
We need more Europe, we need more Union, and we need more fairness in our taxation policy.
Fifth: We have to step up the work for a fair and truly pan-European labour market. Fairness in this context means promoting and safeguarding the free movement of citizens as a fundamental right of our Union, while avoiding cases of abuses and risks of social dumping.
Labour mobility is welcome and needed to make the euro area and the single market prosper. But labour mobility should be based on clear rules and principles. The key principle should be that we ensure the same pay for the same job at the same place.
As part of these efforts, I will want to develop a European pillar of social rights, which takes account of the changing realities of Europe’s societies and the world of work. And which can serve as a compass for the renewed convergence within the euro area.
This European pillar of social rights should complement what we have already jointly achieved when it comes to the protection of workers in the EU. I will expect social partners to play a central role in this process. I believe we do well to start with this initiative within the euro area, while allowing other EU Member States to join in if they want to do so.
As said in the Five Presidents’ Report, we will also need to look ahead at more fundamental steps with regard to the euro area. The Commission will present a White Paper on this in spring 2017.
Yes, we will need to set up a Euro Area Treasury over time, which is accountable at European level. And I believe it should be built on the European Stability Mechanism we created during the crisis, which has, with a potential credit volume of €500 billion, a firepower that is as important as the one of the IMF. The ESM should progressively assume a broader macroeconomic stabilisation function to better deal with shocks that cannot be managed at the national level alone. We will prepare the ground for this to happen in the second half of this mandate.
The European Union is a dynamic project. A project to serve its people. There are no winners or losers. We all get back more than we put in. It is one, comprehensive project. This is also a message for our partners in the United Kingdom, which I have very much in my mind when thinking about the big political challenges of the months to come.
A fair deal for Britain
Since I took office, things have become clearer as regards the United Kingdom: before the end of 2017, there will be a referendum on whether Britain remains in the Union or not. This will of course be a decision for voters in the United Kingdom. But it would not be honest nor realistic to say that this decision will not be of strategic importance for the Union as a whole.
I have always said that I want the UK to stay in the European Union. And that I want to work together with the British government on a fair deal for Britain.
The British are asking fundamental questions to and of the EU. Whether the EU delivers prosperity for its citizens. Whether the action of the EU concentrates on areas where it can deliver results. Whether the EU is open to the rest of the world.
These are questions to which the EU has answers, and not just for the sake of the UK. All 28 EU Member States want the EU to be modern and focused for the benefit of all its citizens. We all agree that the EU must adapt and change in view of the major challenges and crisis we are facing at the moment.
This is why we are completing the Single Market, slashing red tape, improving the investment climate for small businesses.
This is why we are creating a Digital Single Market – to make it such that your location in the EU makes no difference to the price you pay when you book a car online. We are modernising the EU’s copyright rules – to increase people’s access to cultural content online while ensuring that authors get a fair remuneration. And just two months ago, the EU agreed to abolish roaming charges as of summer 2017, a move many tourists and travellers, notably from Britain, have been calling for, for years.
This is why we are negotiating trade agreements with leading nations such as the Transatlantic Trade and Investment Partnership. This is why we are opening markets and breaking down barriers for businesses and workers in all 28 EU Member States.
It is my very personal commitment to improve the way in which the Union works with national Parliaments. I have inscribed a duty to interact more closely with national Parliaments in the mission letters of all Members of my Commission. I am convinced that strengthening our relationship with national Parliaments will bring the Union closer to the people that it serves. This is an ambition that I know Prime Minister David Cameron also shares. I am confident that we will be able to find a common answer.
Over a year ago, when I campaigned to become President of the Commission, I made a vow that, as President, I would seek a fair deal for Britain. A deal that is fair for Britain. And that is also fair for the 27 other Member States.
I want to ensure we preserve the integrity of all four freedoms of the Single Market and at the same time find ways to allow the further integration of the Eurozone to strengthen the Economic and Monetary Union.
To be fair to the UK, part of this deal will be to recognise the reality that not all Member States participate in all areas of EU policy. Special Protocols define the position of the UK, for instance in relation to the euro and to Justice and Home Affairs. To be fair to the other Member States, the UK’s choices must not prevent them from further integration where they see fit.
I will seek a fair deal for Britain. I will do this for one reason and one reason alone: because I believe that the EU is better with Britain in it and that Britain is better within the EU.
In key areas, we can achieve much more by acting collectively, than we could each on our own. This is in particular the case for the tremendous foreign policy challenges Europe is currently facing and which I will address in the next part of this speech.
United alongside Ukraine
Europe is a small part of the world. If we have something to offer, it is our knowledge and leadership.
Around a century ago, one in five of the world’s population were in Europe; today that figure is one in nine; in another century it will be one in twenty-five.
I believe we can, and should, play our part on the world stage; not for our own vanity, but because we have something to offer. We can show the world the strength that comes from uniting and the strategic interest in acting together. There has never been a more urgent and compelling time to do so.
We have more than 40 active conflicts in the world at the moment. While these conflict rage, whilst families are broken and homes reduced to rubble, I cannot come to you, almost 60 years after the birth of the European Union and pitch you peace. For the world is not at peace.
If we want to promote a more peaceful world, we will need more Europe and more Union in our foreign policy. This is most urgent towards Ukraine.
The challenge of helping Ukraine to survive, to reform and to prosper is a European one. Ultimately, the Ukrainian dream, the dream of the Maidan is European: to live in a modern country, in a stable economy, in a sound and fair political system.
Over the past twelve months, I have got to know President Poroshenko well, at a Summit, over dinner at his home, during many meetings and countless phone calls. He has begun a transformation of his country. He is fighting for peace. He deserves our support.
We have already done a lot, lending €3.41 billion in three Macro-Financial Assistance programmes, helping to broker a deal that will secure Ukraine’s winter gas supplies and advising on the reform of the judiciary. The EU and all its Member States must contribute if we are to succeed.
We will also need to maintain our unity.
We need unity when it comes to the security of our Eastern Member States, notably the Baltics. The security and the borders of EU Member States are untouchable. I want this to be understood very clearly in Moscow.
We need more unity when it comes to sanctions. The sanctions the EU has imposed on Russia have a cost for each of our economies, and repercussions on important sectors, like farming. But sanctions are a powerful tool in confronting aggression and violation of international law. They are a policy that needs to be kept in place until the Minsk Agreements are complied with in full. We will have to keep our nerve and our unity.
But we must also continue to look for solutions.
I spoke to President Putin in Brisbane at the G20, in a bilateral meeting that went on into the early hours of the morning. We recalled how long we have known each other, how different times had become. A spirit of cooperation between the EU and Russia has given way to suspicion and distrust.
The EU must show Russia the cost of confrontation but it must also make clear it is prepared to engage.
I do not want a Europe that stands on the sidelines of history. I want a Europe that leads. When the European Union stands united, we can change the world.
United in Leadership in Addressing Climate Change
One example of where we Europe is already leading is in our action on climate change.
In Europe we all know that climate change is a major global challenge – and we have known for a while now.
The planet we share – its atmosphere and stable climate – cannot cope with the use mankind is making of it.
Some parts of the world have been living beyond their means, creating carbon debt and living on it. As we know from economics and crisis management, living beyond our means is not sustainable behaviour.
Nature will foot us the bill soon enough. In some parts of the world, climate change is changing the sources of conflict – the control over a dam or a lake can be more strategic than an oil refinery.
Climate change is even one the root causes of a new migration phenomenon. Climate refugees will become a new challenge – if we do not act swiftly.
The world will meet in Paris in 90 days to agree on action to meet the target of keeping the global temperature rise below 2 degrees Celsius. The EU is on track and made a clear pledge back in March: a binding, economy-wide emissions reduction target of at least 40% by 2030, compared to 1990 levels. This is the most ambitious contribution presented to date.
Others are following, some only reluctantly.
Let me be very clear to our international partners: the EU will not sign just any deal. My priority, Europe’s priority, is to adopt an ambitious, robust and binding global climate deal.
This is why my Commission and I have been spending part of this first year in drumming support for ambition in Paris. Last May I was in Tokyo where I challenged Prime Minister Abe to work with us in ensuring that Paris is a worthy successor of Kyoto.
In June at the G7 summit, leaders agreed to develop long-term low-carbon strategies and abandon fossil fuels by the end of the century.
Later I met Chinese Premier Li Keqiang to prepare Paris and to launch a partnership to ensure that cities of today are designed to meet the energy and climate needs of tomorrow.
And, in coordination with the High Representative, the members of the College have been engaged in climate diplomacy efforts. Today Commissioner Arias Cañete is in Papua New Guinea discussing the plans for Paris with the leaders of the Pacific Islands Forum. If corrective action is not taken to tackle climate change, the tide will rise and those islands will be the proverbial canary in the coalmine.
However, if Paris delivers, humanity will, for the first time, have an international regime to efficiently combat climate change.
Paris will be the next stop but not the last stop. There is a Road to Paris; but there is also a Road from Paris.
My Commission will work to ensure Europe keeps leading in the fight against climate change. We will practice what we preach.
We have no silver bullet to tackle climate change. But our laws, such as the EU Emissions Trading Scheme, and our actions have allowed us to decrease carbon emissions whilst keeping the economy growing.
Our forward-looking climate policy is also delivering on our much needed Energy Union goals: it is making us a world leader in the renewable energy sector, which today employs over one million people across the EU and generates €130 billion turnover, including €35 billion worth of exports. European companies today hold 40% of all patents for renewable technologies and the pace of technological change increases the potential for new global trade in green technology.
This is why a strategic focus on innovation and on interconnecting our markets is being given in the implementation of the Energy Union.
This is what I promised you last year and this is what this Commission has delivered and will continue to deliver.
The fight against climate change will not be won or lost in diplomatic discussions in Brussels or in Paris. It will be won or lost on the ground and in the cities where most Europeans live, work and use about 80% of all the energy produced in Europe.
That is why I have asked President Schulz to host the Covenant of the Mayors meeting in the Parliament next month, bringing together more than 5,000 European mayors. They have all pledged to meet the EU CO2 reduction objective. I hope that all members of this House will lend their support to the action that communities and localities across Europe are taking to making Paris and its follow up a success.
Conclusion
Mr President, Honourable Members,
There were many things I did not and could not mention today. For example, I would have liked to talk to you about Cyprus and my hope, my ambition and my wish to see the island united next year. After I met for a long talk with Presidents Nikos Anastasiades and Mustafa Akinci in the middle of the Green Line in July, I am confident that, with the necessary vision and political will from the two leaders, this is feasible under the current conditions and with continued good coordination between UN and EU efforts. I will offer all my support and assistance to help achieve this objective. Because I believe that walls and fences have no place in an EU Member State.
I have not spoken about Europe’s farmers who were protesting this week in Brussels. I agree with them that there is something wrong in a market when the price of a litre of milk is less than the price of a litre of water. But I do not believe that we can or should start micromanaging the milk market from Brussels. We should compensate the farmers who are suffering from the effects of sanctions against Russia. And this is why the Commission is putting a €500 million solidarity package for farmers on the table. And European and national competition authorities should take a close look into the structure of the market. Something has turned sour in the milk market. My impression is that we need to break some retail oligopolies.
There is much more to be said but in touching upon the main issues, the main challenges confronting us today, for me there is one thing that becomes clear: whether it is the refugee crisis we are talking about, the economy or foreign policy: we can only succeed as a Union.
Who is the Union that represents Europe’s 507 million citizens? The Union is not just Brussels or Strasbourg. The Union is the European Institutions. The Union is also the Member States. It is national governments and national Parliaments.
It is enough if just one of us fails to deliver for all of us to stumble.
Europe and our Union have to deliver. While I am a strong defender of the Community method in normal times, I am not a purist in crisis times – I do not mind how we cope with a crisis, be it by intergovernmental solutions or community-led processes. As long as we find a solution and get things done in the interest of Europe’s citizens.
However, when we see the weaknesses of a method, we have to change our approach.
Look at the relocation mechanism for refugees we put on the table for Greece and Italy in May: the Commission proposed a binding, communitarian solidarity scheme. Member States opted instead for a voluntary approach. The result: the 40,000 figure was never reached. Not a single person in need of protection has been relocated yet and Italy and Greece continue to cope alone. This is simply not good enough.
Look at intergovernmental solutions like the 2011 Fiscal Compact to strengthen fiscal discipline or the 2014 Agreement setting up a common bank resolution fund. Today, we see that not a single Member State has completely implemented the Fiscal Compact. And only 4 out of 19 Member States have ratified the agreement on the bank resolution fund, which is meant to be launched on 1 January 2016.
This is simply not good enough if we want to cope with the present, immense challenges.
We have to change our way of working.
We have to be faster.
We have to be more European in our method.
Not because we want power at European level. But because we need urgently better and swifter results.
We need more Europe in our Union.
We need more Union in our Union.
All my life, I have believed in Europe. I have my reasons, many of which I know and am relieved are not relatable to generations today.
Upon taking office, I said I want to rebuild bridges that had started to crumble. Where solidarity had started to fray at the seams. Where old daemons sought to resurface.
We still have a long way to go.
But when, generations from now, people read about this moment in Europe’s history books, let it read that we stood together in demonstrating compassion and opened our homes to those in need of our protection.
That we joined forces in addressing global challenges, protecting our values and resolving conflicts.
That we made sure taxpayers never again have to pay for the greed of financial speculators.
That hand in hand we secured growth and prosperity for our economies, for our businesses, and above all for our children.
Let it read that we forged a Union stronger than ever before.
Let it read that together we made European history. A story our grandchildren will tell with pride.
European Commission – Speech – [Check Against Delivery]